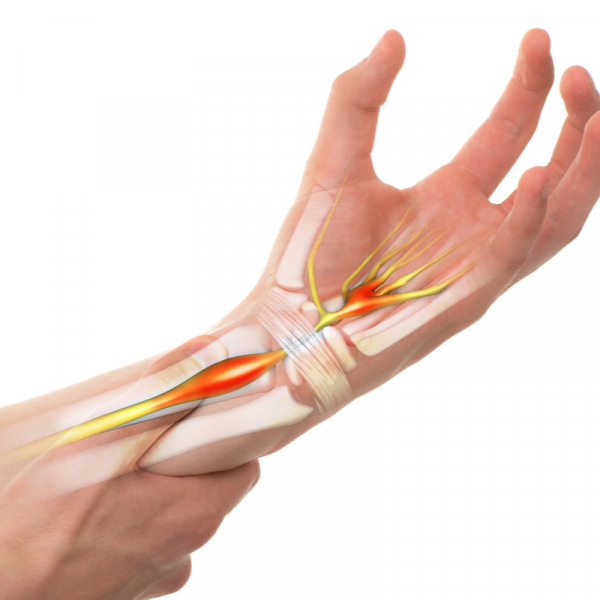
Who is most often affected?
Most people with the disease are in the 50 to 60 age group. However, the incidence among affected women is twice as high as among men. The reason for this is the carpal tunnel, which is usually narrower in women anyway. If pregnancy occurs in the course of life, this increases the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome. Sometimes, narrowing of the carpal tunnel due to pregnancy-related weight gain and associated water retention is already seen in much younger women.
What are the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
In about 40 percent of patients, KTS occurs in both hands. In most cases of the remaining 60 percent, the hand that is mainly used is affected. The first sign of the disease is numbness. This can extend from the thumb over the index finger to the middle finger. The feeling often gets worse when the pressure on the nerve is increased. This often happens at night, as many people sleep with their wrist bent. In the early stages of the disease, this numbness can be dispelled by shaking out the hand and changing the position of the arm. But in the advanced stages, a constant feeling of numbness remains.
How is the disease diagnosed?3
At first suspicion, it is advisable to consult a hand surgeon. The specialist can quickly determine whether carpal tunnel syndrome may be the cause of the symptoms based on the sensitivity to pain and through a palpation examination. In addition to the current mobility of the hand and fingers, information about the duration of the pain is also a helpful diagnostic tool. If there is any suspicion, the surgeon still has the options of measuring the nerve conduction velocity or using an X-ray examination to determine the bony changes. An experienced specialist will soon recognise the diagnosis in this condition.
What happens if I have carpal tunnel syndrome?
The hand only needs to be operated on if the disease is advanced. Mild cases can be treated first. In most cases, anti-inflammatory medication in the form of tablets or cortisone injections is used. In addition, a splint for the hand brings relief to the patient. This is usually only worn at night to prevent the hand from bending during sleep.
What should be done if this therapy does not bring relief?
If this treatment does not give the patient relief, the specialist will probably advise surgery. In the past, this required an incision about ten centimetres long, from the palm down to the forearm. Today, doctors have advanced surgical options at their disposal. Thanks to modern mini-surgery technology, an endoscopic procedure only requires an incision about two centimetres long. During the ten-minute operation, the carpal ligament is first cut. This gives the nerve more space and allows it to regenerate. After an operation for carpal tunnel syndrome, the patient only gets a bandage for one day. After that, he or she should try to use the hand as normally as possible in everyday life.
Is a complete cure possible?
Early treatment of this painful condition is important. However, if the disease is mild at first, the chances of a good healing are good. However, if the carpal tunnel syndrome has already reached an advanced stage, there is unfortunately often already permanent damage to the muscles. After an operation, most complaints are usually noticeably better immediately.
How can you prevent carpal tunnel syndrome from developing?
The best way to prevent this condition is to avoid poor posture of the hands and arms. These would favour the development of this condition. For example, working at a computer encourages such bad postures. It is therefore important to regularly loosen the hands by circling them or shaking them out vigorously. Special stretching exercises and hand gymnastics can also prevent the onset of carpal tunnel syndrome.
