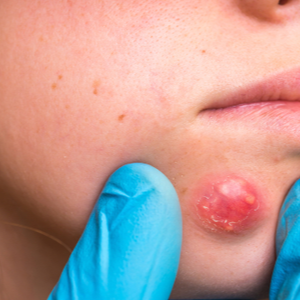
What is a carbuncle?
Carbuncles, colloquially also called boils, are deeper skin infections that arise from several adjacent hair follicles or a series of adjacent boils. Carbuncles are accompanied by severe pain, fever and inflammation of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis). They lead to deep pus accumulation and scarring of the skin. Carbuncles usually form on the neck, back, shoulders, hips and thighs. A carbuncle is usually removed surgically. Aftercare of a carbuncle is done with warm compresses and often oral antibiotics against the bacteria that causes it, Staphylococcus aureus.
What is the difference between a boil and a carbuncle?
A boil is a purulent skin infection caused by bacteria and can easily be mistaken for a large pustule. However, unlike a pimple, a boil is located in deeper layers of the skin and is therefore much more painful, especially since the hair follicle and the surrounding connective tissue are also inflamed in a boil. In technical language, a boil is therefore also called folliculitis. A carbuncle, on the other hand, is caused by the fusion of several neighbouring boils into a larger pus focus. Carbuncles often develop in the neck area and reach deeper into the skin layers than a boil.
How does a carbuncle develop?
A carbuncle is a fusion of several boils into one large inflamed lump. A boil is an inflammation of the hair follicle that not only reaches deep into the hair follicle, but also spreads to the surrounding tissue. In most cases, a carbuncle is caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, which can invade the hair follicle especially in cases of poor hygiene or in patients with a weakened immune system. A carbuncle causes considerable pain and its development can be promoted by the following factors:
- Diabetes mellitus,
- Immunodeficiency diseases such as AIDS,
- poor hygiene,
- greasy skin care products, which can contribute to the clogging of the hair follicles and thus to the development of a furuncle or carbuncle.
What are the symptoms of a carbuncle?
A carbuncle appears as a board-hard, bacterial inflammation of the skin (phlegmon) and causes swelling and severe redness, in the centre of which in some cases even a pustule appears. Initially, the swelling is palpable as a hard lump that can be up to two centimetres in circumference. Over time, pus accumulates under the swelling and the lump becomes more mobile. In addition, there may be a feeling of heat around the site of inflammation. If the carbuncle is left untreated for a long time, it can even cause inflammation of the lymph vessels (local lymphangitis) and fever and a general feeling of fatigue.
How is a carbuncle diagnosed?
For effective treatment of carbuncles, it is important to distinguish the skin infection from similar conditions such as erythrasma or phlegmon. These conditions are often caused by different germs and therefore require different medical and antibiotic treatment. In order to identify a carbuncle without a doubt, the doctor will take a swab of the affected skin and test it for Staphylococcus aureus.
How is a carbuncle treated?
A carbuncle must always be treated medically and should never be cut open by yourself. Self-medication increases the risk of re-infection and spread of the pathogen. If a carbuncle is left untreated, it can lead to inflammation of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis) or even to life-threatening blood poisoning (sepsis).
For effective treatment of a carbuncle, the doctor will usually surgically remove the carbuncle by splitting it. This involves clearing out dead skin cells (necrosis) and removing the pus cavities by drainage. In addition, the patient is usually given a broad-spectrum antibiotic to prevent a new infection. Depending on the dimension and body site where the carbuncle has occurred, strict bed rest may also be prescribed in order to prevent germs from a burst carbuncle from being transferred to other body sites by moving as little as possible. In addition, a disinfecting ointment or solution with the active ingredient polyvidone iodine can support the healing process.
How can the development of a carbuncle be prevented?
The development of carbuncles can be prevented by the following simple hygiene measures:
- washing hands frequently and then drying them thoroughly,
- Avoiding skin-irritating detergents,
- regularly disinfecting the skin after every shave,
- Wearing clothes made of high-quality and absorbent materials,
- changing clothes, bed linen and towels regularly to prevent the accumulation of bacteria,
- Use of cosmetics that do not agglutinate the hair follicles and thus counteract the development of boils.
