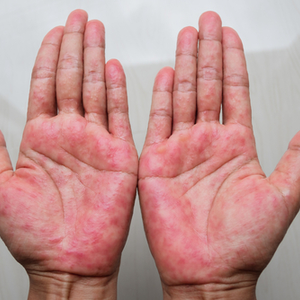
What is dermatitis?
Dermatitis is an inflammatory skin reaction that indicates a disturbed skin barrier. It can be triggered by both internal and external stimuli. Besides a warm and humid room climate, skin rubs can also lead to dermatitis. Typical symptoms of dermatitis are reddened skin, whitish scales, weeping blisters and/or pus and crust formation. Doctors distinguish between different types of dermatitis, for example neurodermatitis or seborrhoeic eczema. Seborrhoeic dermatitis, for example, is characterised by greasy, yellowish scales that appear mainly on the head and face.
What are the symptoms of dermatitis?
Dermatitis is often manifested by the following skin changes:
What types of dermatitis are there?
The term dermatitis refers to a variety of inflammatory skin diseases. Atopic dermatitis and allergic dermatitis are the most common types of skin diseases. Atopic dermatitis is also called neurodermatitis and often begins in infancy with cradle cap on the scalp or face. With advancing age, the upper body, elbows, knees, face and hands are also affected by the skin disease. Typical signs here are very dry, sensitive skin, which can sometimes be accompanied by very itchy eczema.
Allergic dermatitis, on the other hand, involves allergic skin reactions, for example to known allergens such as latex, nickel or perfume. If the skin comes into contact with these allergens, an itchy rash usually forms within the next few days. The rash is usually limited to the area of the skin that came into contact with the allergen (contact dermatitis). If, on the other hand, a food allergy is present, allergic dermatitis can also occur over a large area.
On which parts of the body can dermatitis occur?
Doctors distinguish between different forms of dermatitis. Depending on the type, dermatitis can occur on different parts of the body. For example, nappy dermatitis occurs in the places where the nappy fits, namely the bottom, the genitals and the lower abdomen. If it is a so-called intertrigo, dermatitis occurs on the parts of the body where skin rubs predominantly, for example inside the skin folds.
What external influences can trigger dermatitis?
Dermatitis can be caused by different influences. Often there can be several triggers at the same time to which the skin reacts. These include, for example:
- Moisture can soften skin protection and contribute to inflammation, especially if the skin does not get enough air to breathe. This can happen, for example, when wearing a nappy or staying in water for a long time.
- Irritating substances such as acids or other aggressive substances that get on the skin can also promote dermatitis. These include, for example, hair dyes or disinfectants.
- Allergic dermatitis can be caused by allergens. In this case, either a contact eczema or an allergic reaction can develop. Contact dermatitis is when the skin has come into direct contact with the allergic substance.
- Prolonged friction of the skin leads to overstressing of the skin barrier. If the stressed skin area becomes inflamed, the doctors speak of an intertrigo.
- The skin can become inflamed due to pressure, for example from one's own weight. Bedridden people, but also people in wheelchairs, can therefore easily develop a so-called decubitus.
- In the case of an infection, the skin barrier and the natural acid mantle of the skin are also impaired. As a result, viruses, bacteria, but also fungal spores and/or parasites can accumulate in the upper layers of the skin and trigger an inflammation there.
How is dermatitis treated?
The specific treatment of dermatitis always depends on its causes and severity. If it is a recurring rash, a dermatologist should be consulted in any case. This is because it is possible that allergic dermatitis or atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis) is hidden behind it.
In most cases, dermatitis can be treated well with an appropriate ointment or cream. Ointments with zinc oxide and an antifungal agent have proven to be particularly effective. In addition, zinc oxide can dry out the affected skin area, reduce the inflammation and inhibit the multiplication of bacteria. In rare cases, doctors may also prescribe antibiotics. If the dermatitis is particularly severe, light therapy may be prescribed.
How can dermatitis be prevented?
If you suffer from recurrent dermatitis, the following tips could help prevent it in the future:
- identify the personal triggers of dermatitis and avoid them. This could include certain foods, for example.
- wear breathable clothing and only high-quality materials,
- Avoid skin care products with preservatives and fragrances,
- avoiding showers that are too long and too hot,
- use cooling gels and lotions to relieve itching,
- Avoid and reduce stress as much as possible.
