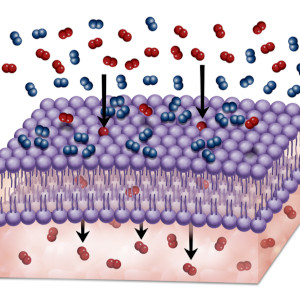
Electro-operation is a method that is often used in molecular biology. The aim is to make the cell membrane temporarily permeable (permeable) in order to introduce DNA into prokaryotic cells or eukaryotic cells.
This is done by an electric field, usually generated as a short pulse by the discharge current of a capacitor, which permeabilises the cells due to various effects.
If we now look at the treatment of blood with a low-current treatment, we produce exactly the same effect in principle due to the current flow, i.e. the pores of the cell walls of the blood cells become more permeable for substances floating in the blood plasma for a short time.
Due to this permeability, toxic concentrations can occur inside the cells of the red blood cells.
Experienced therapists advise that the electromedical treatment should only be carried out if the last food intake was at least 4 hours before.
This fasting state is best achieved early in the morning, before taking any orthomolecular or medicinal substances.
A drug taken shortly before or during treatment could suddenly cause toxic symptoms such as nausea or vomiting.
Since the cell walls return to their original state very quickly after treatment and are therefore no longer permeable, the patient can take substances again without hesitation just half an hour after treatment.
In this context, it is important to warn against taking garlic during electrotherapy.
Garlic contains a substance called sulphonhydroxyl. This substance crosses the blood-brain barrier and poisons brain cells due to its toxicity.
