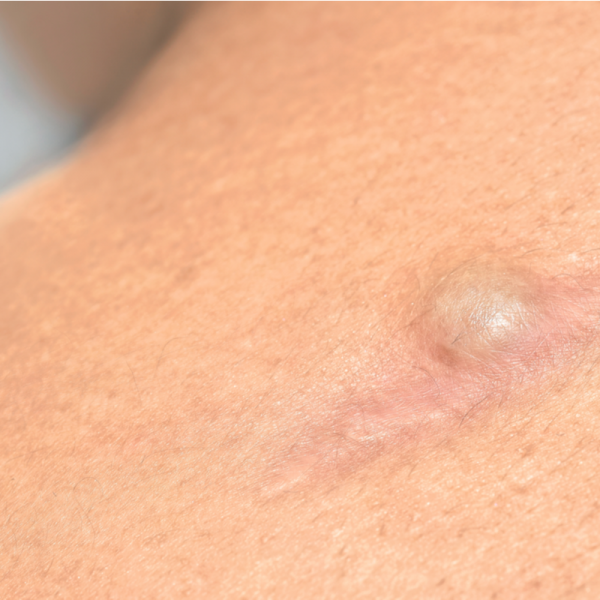
What is an epidermoid cyst?
An epidermoid cyst develops in the dermis, under the surface of the skin, and is recognisable as a small bump. An epidermoid cyst can range from 1 to 4 cm in circumference and can appear in many different parts of the body. However, the epidermoid cyst is most often found on the face, trunk or neck. The terms "epidermal cyst", "epidermal bullet cyst" or "infundibular cyst" are often used as synonyms for the epidermoid cyst. In general, an epidermoid cyst is usually harmless and benign.
How does an epidermoid cyst develop?
The first layer of skin, i.e. the surface of the skin, is the epidermis. It consists of basal cells, melanocytes, squamous cells, cells of the immune system and the so-called Merkel cells. Below the epidermis is the dermis, a thin layer of tissue, which is also called the basement membrane. It contains nerves and blood vessels. Under the dermis is the subcutaneous fat, a layer of fat also called subcutaneous adipose tissue.
Although the exact cause of an epidermoid cyst is still unknown, doctors assume that it can be triggered by trauma. This is the case, for example, when a piece of the epidermis is pressed into the dermis. However, it is also conceivable that an epidermoid cyst develops as an inflammation of a hair follicle.
What are the symptoms of an epidermoid cyst?
An epidermoid cyst is usually felt for years as a small swelling under the skin and then develops into small nodules. When the epidermoid cyst ruptures or bursts, it can cause pain or inflammation. Inflammation is caused when the keratin inside the cyst spills onto the surrounding tissue. Keratin is the product of the epidermis that makes the skin tough and waterproof and protects it from injury and toxins.
How is an epidermoid cyst diagnosed?
A definite diagnosis of an epidermoid cyst is usually only made after the cyst has been surgically removed. This is because the cyst is then sent to a pathologist for a biopsy, who will find the so-called epithelium if the result is positive. This is a round structure surrounded by a keratinising squamous epithelium. There may be keratin residues inside the cyst.
How is an epidermoid cyst treated?
In many cases, an epidermoid cyst does not require specific treatment. If it causes discomfort, it can be removed surgically if necessary. If inflammation is present, the epidermoid cyst can be drained through an incision. If it subsequently recedes, it is usually removed surgically. However, one should wait at least one month before surgery if the cyst was inflamed.
Epidermoid cyst frequencies
|
Pathogen |
Source |
Frequencies |
|
Epidermoid cyst |
EDTFL |
Members get access to the frequencies immediately after registration. |
