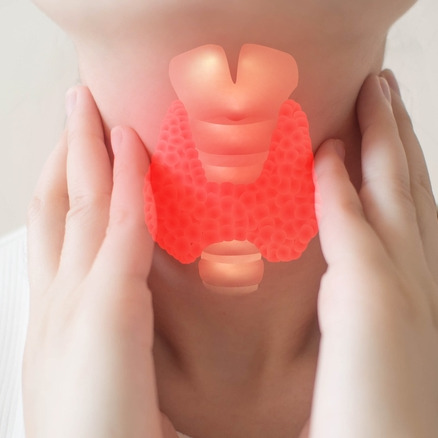
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
A comprehensive guide to autoimmune thyroid disease
Dear readers,
Today we would like to address a topic that affects many people but is often not recognised straight away:
hashimoto's thyroiditis.
This autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland is named after Hakaru Hashimoto, who first described it, and is a chronic inflammation that can have long-term effects on health.
In this article, you will learn all about the causes, symptoms and treatment options for this disease so that you are well informed and can take the necessary steps if you or someone close to you is affected.
What is Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and, over time, often to hypothyroidism[0]. The thyroid gland is a small organ in the front of the neck that produces hormones that are essential for regulating the metabolism.
Causes and risk factors
The exact causes of Hashimoto's thyroiditis are not yet fully understood, but it is thought that a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors play a role. Women are more commonly affected than men and the condition often occurs in midlife, but can also occur in other age groups[0].
Recognising symptoms
The symptoms of Hashimoto's can be varied and usually develop slowly over years.
Initially, they can be non-specific and often include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, hair loss and constipation.
As the condition progresses, the thyroid gland may become enlarged, which is known as a goitre[0].
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis is usually based on a combination of blood tests, ultrasound and, if necessary, further examinations.
The blood tests in particular are crucial, as they can provide information about thyroid levels and antibodies that indicate an autoimmune disease[0].
Therapy and treatment
The treatment of Hashimoto's thyroiditis aims to alleviate the symptoms and support thyroid function.
Hormone replacement therapy with L-thyroxine is used when hypothyroidism occurs to compensate for the lack of thyroid hormones[1][2].
The dosage of the medication is customised and often has to be taken for the rest of the patient's life, as the thyroid tissue does not recover once it has been destroyed[2].
Lifestyle and supportive measures
In addition to drug treatment, lifestyle and dietary adjustments can also have a supportive effect.
In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, for example, it is often recommended to eat a diet low in iodine, as iodine can increase the inflammation of the thyroid gland[1][2].
Certain trace elements and vitamins can also be helpful, and it is important to maintain a trusting relationship with the doctor treating you in order to optimise your treatment[1].
Special situations
Pregnancy and the desire to have children
special attention is required if you are pregnant or planning to have children. Women with Hashimoto's thyroiditis should have their thyroid levels monitored closely, as the need for thyroid hormones can change during pregnancy[2].
conclusion
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a serious condition, but it can be managed well with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments. It is important to pay attention to your own body signals and seek medical advice if you suspect you have thyroid disease.
If you would like to find out more about the treatment of Hashimoto's thyroiditis or would like to make an appointment with a specialist, you can find more information and contact details on the websites we have listed in the footnotes[1][2].
we hope that this article has given you a comprehensive understanding of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Stay healthy and take care of yourself!
footnotes:
- [0] NDR Ratgeber - Hashimoto's thyroiditis:
Causes, symptoms and treatment.
Available at:
https://www.ndr.de/ratgeber/gesundheit/Hashimoto-Thyreoiditis-Ursachen-Symptome-und-Behandlung,hashimoto100.html - [1] Hashimoto's thyroiditis - therapy & treatment.
Available at: https: //www.hashimoto-thyreoiditis.de/therapie - [2] University Hospital Zurich - Autoimmune thyroiditis:
Hashimoto's thyroiditis treatment.
Available at: https://www.usz.ch/fachbereich/endokrinologie/angebot/hashimoto-thyreoiditis/
Become a member now
As a member, you will receive further information and frequencies on this topic! Log in here!



